BTK Inhibitors: The Next Frontier in Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Treatment?
By Avisha Jain and Nitin Kumar | Wednesday 18, Sep 2024

Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex autoimmune disorder characterized by the progressive destruction of myelin in the central nervous system. According to WHO, it is estimated that over 1.8 million people have MS worldwide. Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) has emerged as a critical player in the pathogenesis of MS due to its role in immune cell activation and inflammation. This article explores the role of BTK in MS and provides an overview of the BTK inhibitors currently under development, including BIIB091, Evobrutinib, Fenebrutinib, Orelabrutinib, Remibrutinib, and Tolebrutinib.1, 22
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase: A Key Immune Regulator
BTK is a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase essential for B-cell maturation and function. It is also involved in the signalling of other immune cells, such as mast cells, macrophages, and microglia. Given its role in regulating immune responses, BTK is a significant target for therapies aimed at autoimmune diseases like MS.
BTK and Multiple Sclerosis: The Connection2
Immune Cell Activation
In MS, immune cell activation, particularly B cells and microglia, drives myelin destruction. BTK facilitates B-cell receptor signalling, which is crucial for B-cell activation and antibody production. Additionally, BTK's involvement in microglial activation links it to neuroinflammation in MS.
B-Cell Contribution
B cells contribute to MS through antibody production and cytokine release. Targeting BTK can modulate B-cell activity, potentially reducing the autoimmune attack on myelin.
Microglial Activation
BTK is involved in microglial activation, which contributes to neuroinflammation and damage in MS. Inhibiting BTK could help reduce this neuroinflammatory process.
BTK Inhibitors: Current Developments
The development of BTK inhibitors represents a promising strategy for MS treatment. Several BTK inhibitors are under investigation, each with unique properties and potential benefits. The table below provides a comparative overview of these inhibitors based on recent clinical trial data:
| Evobrutinib (75 mg BID) | Tolebrutinib (60 mg QD) | Fenebrutinib (200 mg BID) | Remibrutinib | Orelabrutinib | BIIB091 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | Merck KGaA | Sanofi | Roche | Novartis | Innocare | Biogen |
| Development Phase | P3 (Discontinued) | P3 | P3 | P3 | P2 | P2 |
| BTK Binding3 | Covalent, Irreversible | Covalent, Irreversible | Non-covalent, Reversible | Covalent, Irreversible | Covalent, Irreversible | Non-covalent, Reversible |
| Half Life (h)4 | 2 | 2 | 4.2-9.9 | 1-2 | 4 | 0.66 |
| Relative reductions in Gd+ lesions5,6,7 | -- | Ph2 @12 wks - 89% | Ph2 @12 wks - 90% | -- | Ph2 @12 wks - 92.5% | -- |
| Annualized Relapse Rate8,9,10,11 | Ph2 @48 wks - 0.11 | Ph2 @48 wks - 0.17 | Ph2 @48 wks - 0.04 | -- | -- | -- |
Note: “--" Relevant data for comparison were not available in public domain
Annualized Relapse Rate (ARR) for BTK Inhibitors in MS
Below is a chart showing the Annualized Relapse Rate (ARR) for various BTK inhibitors based on recent clinical trial data:
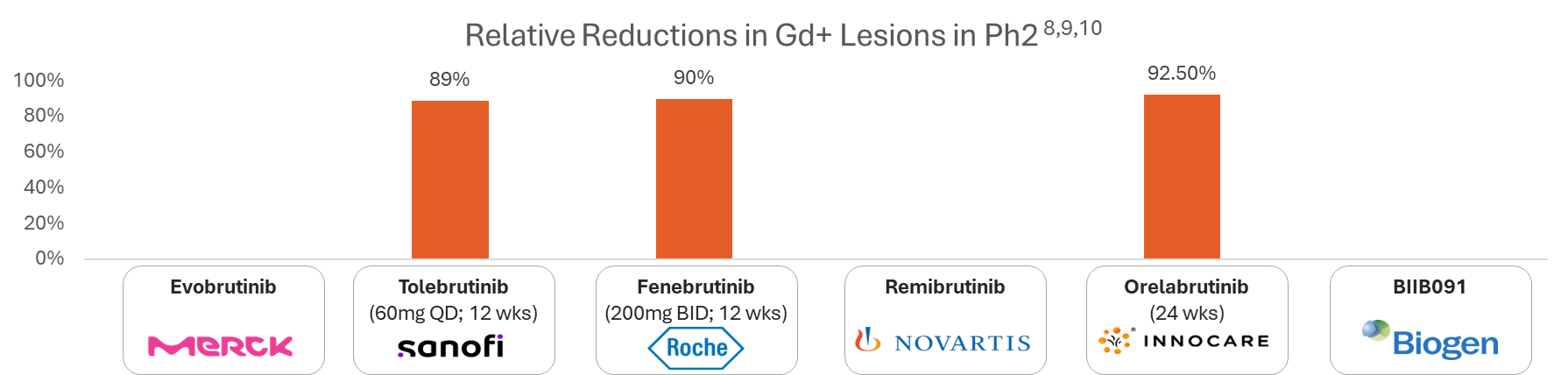
Note: Ph2/Ph3 assets are considered in the analysis
Relative reduction in GD+ Lesion for BTK Inhibitors in MS:
Below is a chart showing the Relative reduction in GD+ lesion for various BTK inhibitors based on recent clinical trial data
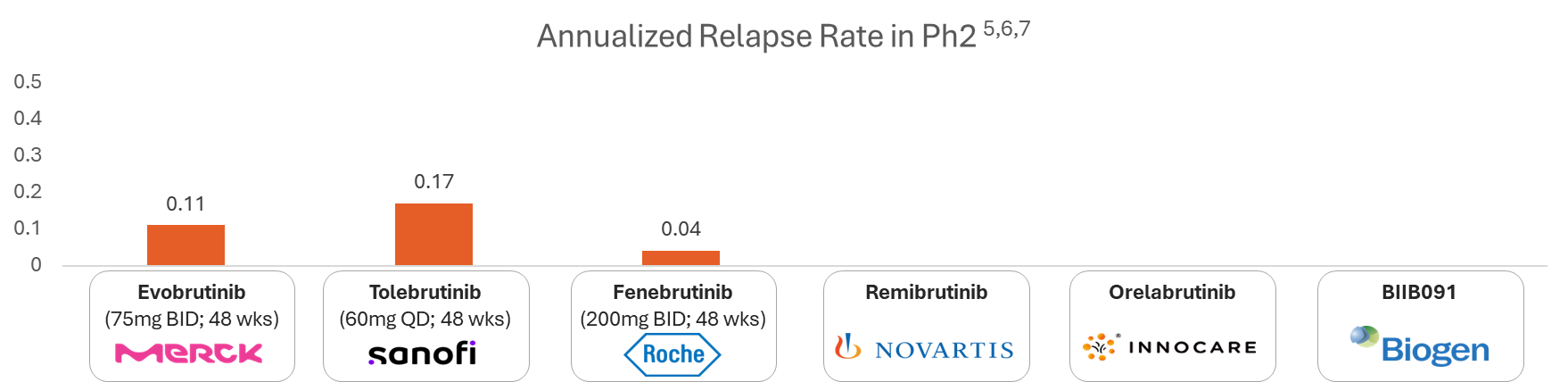
Note: Ph2/Ph3 assets are considered in the analysis
Development Updates
- BIIB091: Biogen's BIIB091 is currently in Phase 2 trials and is showing promise in reducing relapse rates in relapsing MS. The upcoming milestone for BIIB091 includes the completion of Phase 2 trials, which will further assess its efficacy and safety in a larger cohort. Biogen is also exploring the drug's potential benefits in combination therapies.12,13,14
- Evobrutinib: Merck KGaA's Evobrutinib, which is in Phase 3 development, had encountered a significant setback on 6th December 2023. Despite earlier promising results, recent Phase 3 trials have failed to meet their primary endpoints for reducing relapse rates in relapsing MS. This challenge underscores the complexities of drug development and the need for continued innovation in treatment approaches.15
- Fenebrutinib: Fenebrutinib, developed by Genentech/Roche, is advancing through Phase 3 trials. Phase 2 results indicate that Fenebrutinib has met primary endpoints in reducing relapse rates and lesion activity. The next significant milestone will be the final data analysis from ongoing trials, which will help determine its place in the MS treatment landscape and possible filing for regulatory approval. New enrolment for the Phase III trial in the U.S. is paused; enrolment in countries outside of the U.S. continues. Fenebrutinib is currently being investigated in two phase 3 trials, the Phase 3 program includes two identical trials in RMS (FENhance I & II) with an active teriflunomide comparator with results due in 2025 and 2028. If the results are positive, Fenebrutinib will be submitted for regulatory approval.16
- Orelabrutinib: In February 2023, Biogen Inc. ("Biogen") notified the Company of its decision to terminate its licence and collaboration agreement with the Company, an oral small molecule Bruton's tyrosine kinase (“BTK”) inhibitor for the potential treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (“MS”) along with the research and development services. Innocare’s Orelabrutinib has completed Phase 2 trials, focusing on both relapsing and progressive forms of MS. Recent results have shown promise in reducing relapse rates in relapsing MS and mitigating disease progression in progressive forms.17,18
- Remibrutinib:Novartis’s Remibrutinib is in Phase 3 development. The upcoming milestones for Remibrutinib involve further data collection on its efficacy and safety, with a focus on understanding its impact on disability progression and potential approval discussions with regulatory bodies.19
- Tolebrutinib:Tolebrutinib, developed by Sanofi, is in Phase 3 trials. Recent data highlights its ineffectiveness in GEMINI studies 1 and 2, in reducing relapse rates and lesion burden in relapsing MS however, in the HERCULES study, Tolebrutinib achieved the primary goal of delaying the onset of confirmed disability progression in individuals with non-relapsing secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (nrSPMS), a group that currently lacks approved treatments and faces significant unmet medical needs. The next steps include the completion of ongoing studies and preparation for potential regulatory submissions, as well as exploring its effects in combination therapies and different MS subtypes. Phase 3 study results will form the basis for future discussions with global regulatory authorities.20,21
Development timeline of BTK inhibitors in MS:
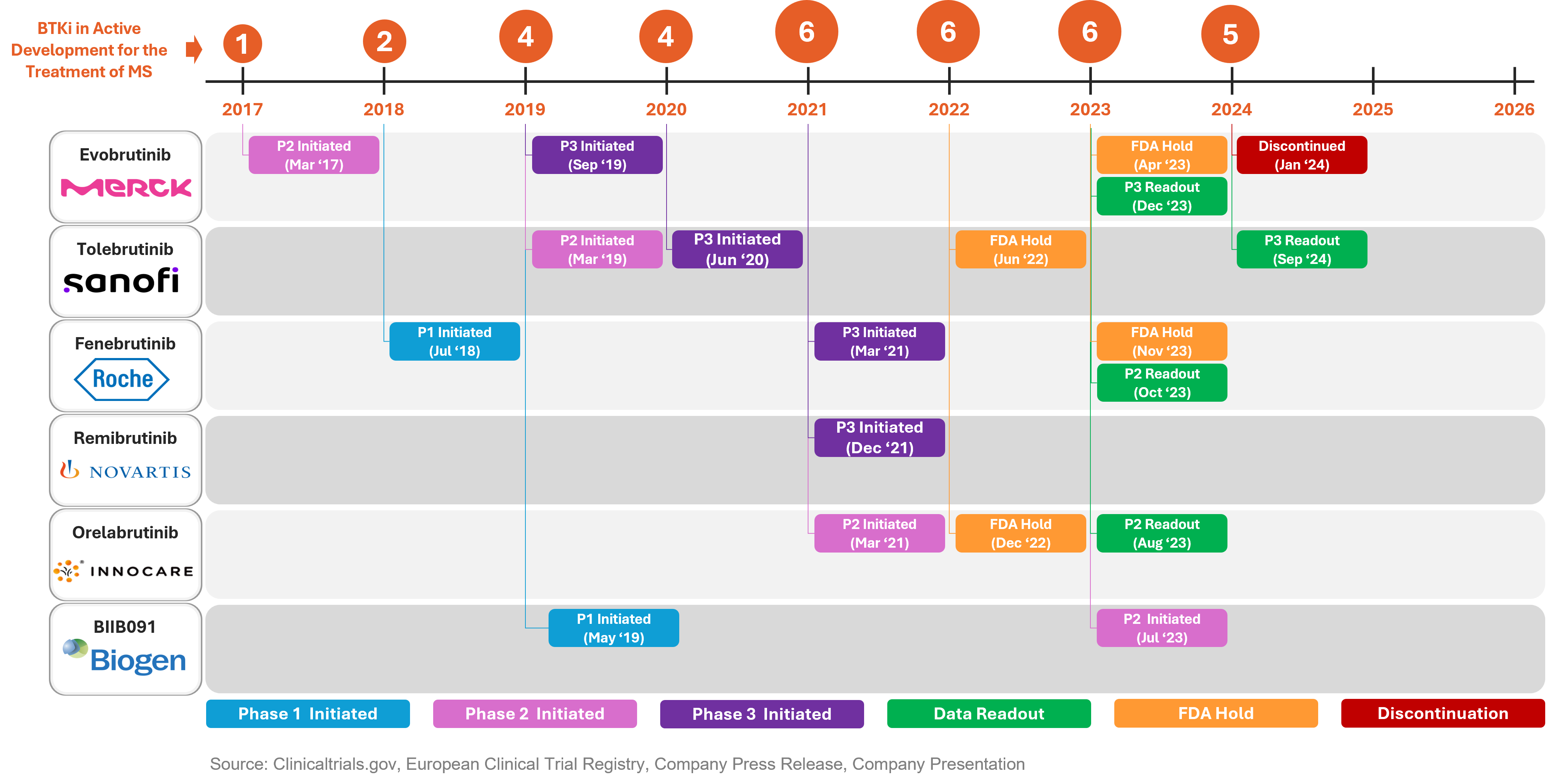
Source: Clinicaltrials.gov, European Clinical Trial Registry, Company Press Releases, Company Presentations
Future Directions and Challenges
The development of BTK inhibitors for MS offers significant promise, but several challenges remain. Long-term safety, optimal dosing regimens, and potential off-target effects need to be thoroughly evaluated. Additionally, understanding how BTK inhibitors perform in different MS subtypes, such as primary progressive and secondary progressive MS, will be crucial for developing personalized treatment strategies.
The development of BTK inhibitors has faced significant challenges due to severe adverse events. The FDA has placed clinical holds on four BTK inhibitors to date. In 2022, Tolebrutinib (Sanofi) and Orelabrutinib (Innocare) were put on hold, followed by Evobrutinib (Merck KGaA) and Fenebrutinib (Roche) in 2023. Elevated liver enzyme levels were the most common side effect observed. Notably, Fenebrutinib is a non-covalent molecule with irreversible bonding, which means it does not form a permanent bond with its target receptor. This characteristic might result in fewer side effects. The impact of these structural differences on safety will become clearer with the Phase 3 trial results.
Ongoing research and clinical trials will provide more insights into the efficacy and safety of these BTK inhibitors. As our understanding of their mechanisms of action deepens, these therapies could play a pivotal role in the future management of MS.
Upcoming presentations of BTK inhibitors in ECTRIMS 2024
| Sr. No. | BTK Inhibitors | BTK Inhibitors Abstract Title | Presentation Date | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Evobrutinib | Targeting Inflammation: Evobrutinib’s Role in Controlling CNS Autoimmune Disease Through B Cell and Myeloid Cell Modulation | 18 Sep. 2024, Wednesday | Poster (P896) |
| 2. | Fenebrutinib | Exposure-response Analysis of Fenebrutinib in Patients with Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis | 18 Sep. 2024, Wednesday | Poster (P1611) |
| Fenebrutinib Maintains Low Disease Activity in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis: Results from the FENopta Trial Open-label Extension | 18 Sep. 2024, Wednesday | Poster (P1612) | ||
| Elucidating the potential of Fenebrutinib, a noncovalent and reversible Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, to modulate microglial inflammation in human brain cell systems | 18 Sep. 2024, Wednesday | Poster (P795) | ||
| 3. | Remibrutinib | Remibrutinib Exposure in Cerebrospinal Fluid: Insights from a Study in Healthy Subjects | Not available | Poster (P1319) |
| 4. | Tolebrutinib | Efficacy and Safety of Tolebrutinib Versus Teriflunomide in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis: Results from the Phase 3 GEMINI 1 and 2 Trials | 20 Sep. 2024, Friday | 20 Sep. 2024, Friday Oral Session (O135) |
| Efficacy and Safety of Tolebrutinib Versus Placebo in Non-Relapsing Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: Results from the Phase 3 HERCULES Trial | 20 Sep. 2024, Friday | Oral Session (O136) |
Source ECTRIMS 2024
Conclusion
Bruton's tyrosine kinase is a key regulator of immune responses involved in multiple sclerosis. The development of BTK inhibitors, such as BIIB091, Fenebrutinib, Orelabrutinib, Remibrutinib, and Tolebrutinib, represents a promising advance in MS treatment. Recent setbacks have been observed with Evobrutinib and Tolebrutinib in RMS. However, Tolebrutinib's Phase 3 data from the HERCULES trial showed positive results in non-relapsing secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Additionally, Fenebrutinib's Phase 2 OLE data from the FENopta study indicated near-complete suppression of disease activity and disability progression for up to 48 weeks in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. These drugs offer the potential to significantly alter the course of the disease by targeting underlying immune mechanisms. As research progresses, these therapies may provide new and effective options for managing MS, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this challenging condition.
References
| Sr. No. | References | Sr. No. | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mayo Clinic | 13. | Diana Gallagher- Biogen MD.2023 |
| 2. | Laura Airas et al, Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024 | 14. | Eris Bame et al, Clin Transl Immunology. 2021 |
| 3. | Dalia L Rotstein, Mult Scler. 2022 | 15. | Merck PR-Dec 2024 |
| 4. | Avinash Kolli et al, Practical Neurology, 2023 | 16. | Roche PR-Nov 2023 |
| 5. | Tolebrutinib - Prof. Daniel S Reich, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2021 Sep | 17. | Innocar Orelabrutinib |
| 6. | Fenebrutinib – Bar-Or Amit et al, Neurology 2024 | 18. | Innocare Annual Report-2023 |
| 7. | Orelabrutinib – Innocare Annual Report 2023 | 19. | Clinical Trial for Safety and efficacy of Remibrutinib |
| 8. | Evobrutinib – Montalban X et al, Multiple Sclerosis, 2024 | 20. | Sanofi PR-Sep 2024 |
| 9. | Tolebrutinib – Sanofi PR – Oct 2021 | 21. | Sanofi Presentation 2022 |
| 10. | Fenebrutinib – Roche PR – Sep 2024 | 22. | WHO – MS Key Facts |
| 11. | Sanofi PR – Sep 2024 | 23. | Aubagio US Label |
| 12. | Biogen SEC filings-2023 |